Neutron stars and the secret lives of quarks
Neutron stars and the secret lives of quarks
View
Abstract
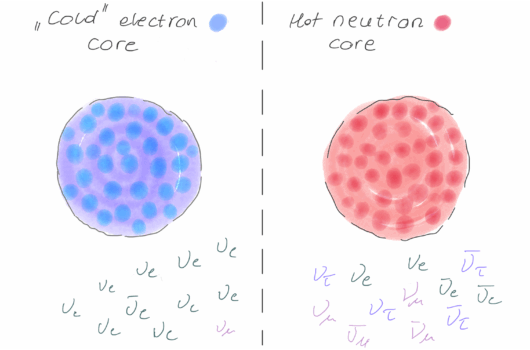
The discovery of non-diffuse sources of gravitational waves through compact-object mergers opens new prospects for the study of physics beyond the Standard Model. In this Letter, we consider the implications of the observation of GW190814, involving a coalescence of a black hole with a ![]() compact object, which may be too massive to be a neutron star, given our current knowledge of the nuclear matter equation of state. We consider the possibility of a new force between quarks, suggested in other contexts, that modifies the neutron star equation of state, particularly at supranuclear densities. We evaluate how this modification can impact a neutron star’s mass and radius to make the observed heavy compact object more probably a neutron star, rather than a black hole, and suggest that further such objects may yet be found. We note the terrestrial and astrophysical measurements that could confirm our picture.
compact object, which may be too massive to be a neutron star, given our current knowledge of the nuclear matter equation of state. We consider the possibility of a new force between quarks, suggested in other contexts, that modifies the neutron star equation of state, particularly at supranuclear densities. We evaluate how this modification can impact a neutron star’s mass and radius to make the observed heavy compact object more probably a neutron star, rather than a black hole, and suggest that further such objects may yet be found. We note the terrestrial and astrophysical measurements that could confirm our picture.