Featured Research Articles
-
post
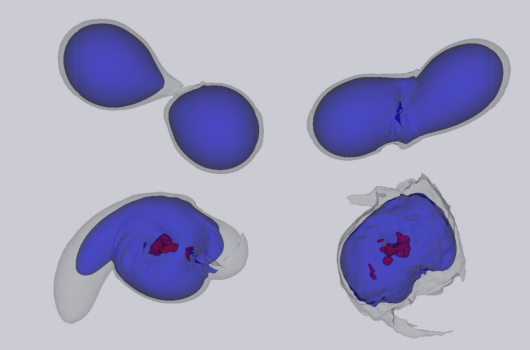
Neutron Star Wars: The Strong Force Awakens
A long time ago in a galaxy far, far away, two neutron stars entered a collision course. Locked in an orbit around each other for millions of years, their separation became shorter as they revolved faster [...]
-
post
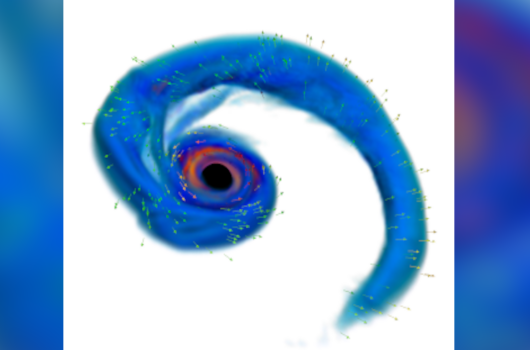
Electromagnetic Signatures from the Tidal Tail of a Black Hole – Neutron Star Merger
Black hole – neutron star (BH-NS) mergers are a major target for ground-based gravitational wave (GW) observatories. In its third observing run, the GW detector network (advance LIGO, Virgo, KAGRA) […]
-
post
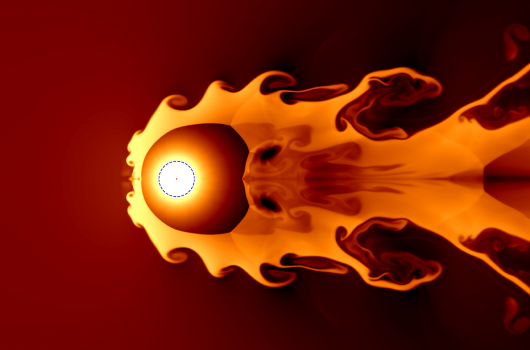
r-Process Radioisotopes from Near-Earth Supernovae and Kilonovae
Near-Earth explosive events are inevitable. Supernovae (SN) explode in our Milky Way roughly every ∼ 30 year (yr) on average. This suggests that supernova explosions within 100 pc of Earth are expected to have occurred every few Myr.
-
post
The Secret Lives of Quarks: Hints of New Forces in Neutron Stars
At the ends of their lives, heavy stars can no longer support their own weight, which can result in fantastically energetic explosions, i.e., supernovae. When the stardust settles, the heaviest […]
-
post
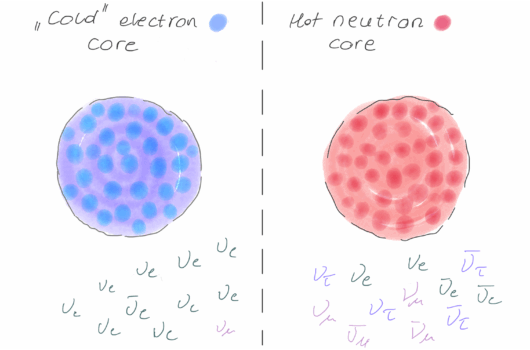
Using Software to Simulate Neutrino Flavor Instability
A fantastic amount of neutrinos are emitted during cataclysmic astrophysical explosions like core-collapse supernovae and neutron star mergers. In both cases, the emitted neutrinos drive outflows that end up enriching […]